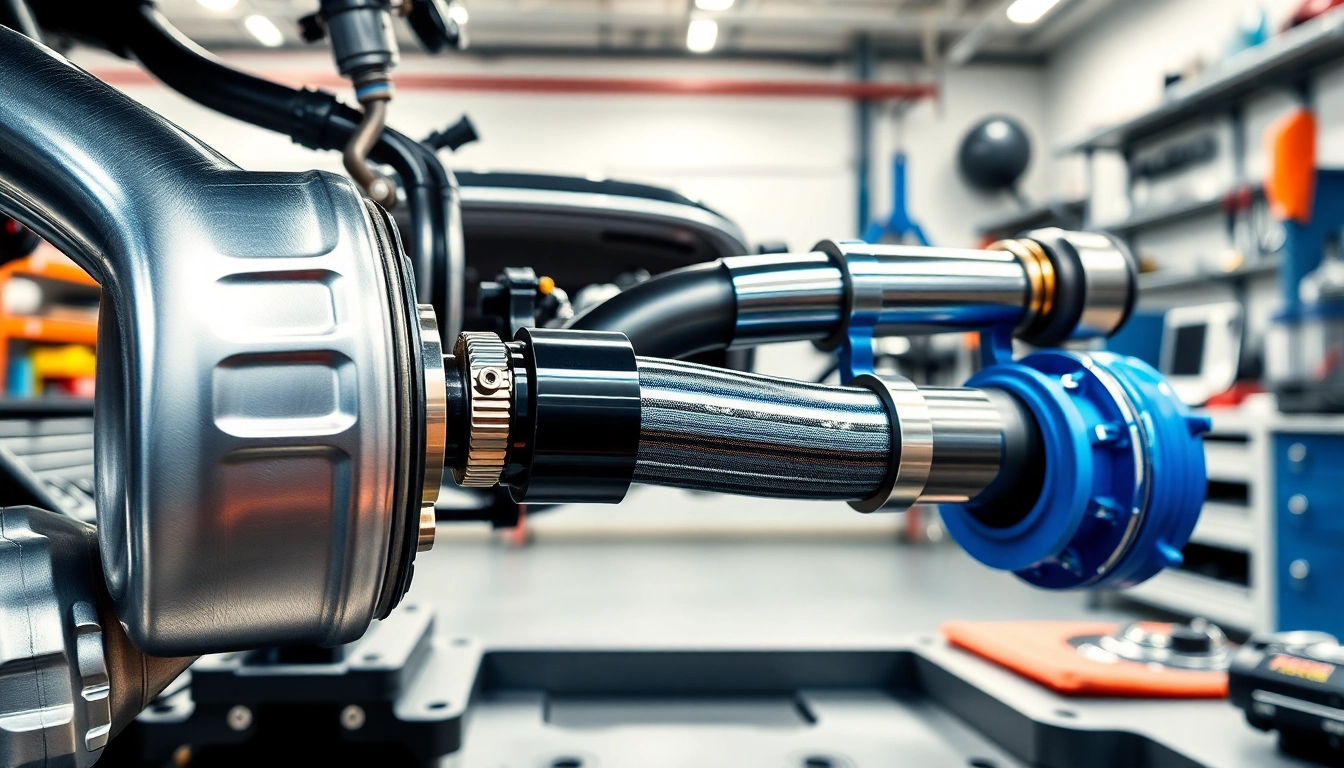
1. Introduction to What is a Charge Pipe
A charge pipe is an integral part of turbocharged automotive systems, playing a pivotal role in enhancing engine performance and overall efficiency. As vehicles have evolved and the demand for increased power and efficiency has risen, understanding the function and significance of various components within the engine has become more critical. In this article, we will delve deep into what is a charge pipe, exploring its definition, components, and material characteristics.
The what is a charge pipe serves as a vital link between the turbocharger and the engine, enabling the transfer of compressed air at high temperatures. Knowing the specifics about charge pipes helps enthusiasts and drivers alike to recognize their importance in the performance landscape of modern vehicles.
1.1 Definition and Purpose
At its core, a charge pipe is a component specifically designed to carry pressurized air from the turbocharger to the intake manifold of an engine. This pressurized air is crucial for increasing combustion efficiency, resulting in improved engine performance. The primary purpose of charge pipes is to enable a quick and efficient pathway for air that has been compressed by the turbo, ensuring that the engine receives the necessary airflow for optimal combustion.
1.2 Components of a Charge Pipe System
A typical charge pipe system includes several essential components:
- Charge Pipes: These are the main conduits for compressed air and are typically located between the intercooler and the engine intake.
- Intercoolers: Intercoolers lower the temperature of the compressed air before it enters the engine for improved density and performance.
- Diverter or Blow-Off Valve: These valves release excess pressure to prevent over-boost conditions, stabilizing the system during various driving conditions.
- Silicone Hoses and Clamps: Often used to connect different components within the charge pipe system, these fittings are vital for durability and leak prevention.
1.3 Common Materials Used
Charge pipes can be constructed from various materials, with each offering unique advantages:
- Aluminum: Lightweight and highly resistant to corrosion, aluminum charge pipes are popular for their durability and improved performance.
- Stainless Steel: Known for its strength and ability to withstand high temperatures, stainless steel is ideal for handling the demanding environments of turbocharged engines.
- Silicone: Often used for connectors and bends, silicone provides flexibility and is resistant to heat and pressure, making it an excellent choice for high-performance applications.
2. How Charge Pipes Work in Turbocharged Engines
2.1 Airflow Process Explained
Understanding the airflow process within turbocharged engines is vital to appreciate the role of charge pipes. When the engine is running, air is drawn into the turbocharger, where it is compressed. This compression heats the air, increasing its density, and then the heated air flows into the intercooler. Here, the air is cooled before traveling through the charge pipe and into the intake manifold.
2.2 Connection with Other Engine Components
A charge pipe connects seamlessly with various engine components to facilitate optimal airflow. For example:
- Turbocharger: It supplies the compressed air that travels through the charge pipe.
- Intercooler: It cools the heated compressed air to enhance efficiency before it reaches the engine.
- Intake Manifold: This component receives the cooled, compressed air from the charge pipe to mix with fuel for combustion.
2.3 Importance of Proper Installation
Proper installation of charge pipes is essential to prevent leaks and ensure that the system operates efficiently. Misalignments or poor connections can lead to air leaks, reducing engine performance and potentially causing engine damage. It is crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines and use appropriate tools during installation to achieve the best results.
3. Benefits of Upgrading to High-Performance Charge Pipes
3.1 Performance Enhancements
Upgrading to high-performance charge pipes can lead to significant enhancements in overall engine performance. These improvements typically include:
- Increased Airflow: High-performance charge pipes often feature larger diameters and smoother bends, facilitating improved airflow and reducing turbulence.
- Boost Response: A more efficient path for air helps the turbocharger spool faster, resulting in reduced turbo lag and quicker acceleration.
- Improved Cooling Efficiency: Many upgraded options come with better thermal properties, helping to maintain optimal air temperatures for increased performance.
3.2 Durability and Reliability Improvements
High-performance charge pipes are usually made from stronger materials than factory-installed options, ensuring that they can withstand extreme operating conditions without failure. This enhanced durability translates to longer-lasting components that can handle increased pressure from boosted engines. Drivers can enjoy peace of mind knowing their charge pipes are less likely to burst or leak under stress.
3.3 Enhanced Engine Response
As charge pipes improve the flow of air into the engine, they contribute significantly to enhanced throttle response. Drivers will often notice a more immediate and lively reaction to acceleration inputs, making their driving experience more engaging. This responsiveness is crucial for both casual driving and competitive racing scenarios, where every millisecond matters.
4. Common Issues and Troubleshooting with Charge Pipes
4.1 Identifying Leaks and Failures
Leaks in charge pipes can severely affect performance, and identifying them early can save both time and repair costs. Common indicators of a charge pipe leak may include:
- Loss of Power: A noticeable reduction in acceleration or power output can signify an issue.
- Unusual Sounds: Hissing or popping noises may indicate air escaping from a faulty seal or connection.
- Check Engine Light: An illuminated check engine light may be triggered by irregular airflow readings related to leaks.
4.2 Maintenance Tips for Charge Pipes
To ensure longevity and consistent performance, maintaining charge pipes is essential. Here are some tips:
- Inspect for wear and tear regularly, particularly focusing on connections and seals.
- Clean charge pipes periodically to prevent buildup that may hinder airflow.
- Ensure all clamps and fittings are tightened properly to prevent leaks.
4.3 When to Consider Replacement
Replacing charge pipes may become necessary if they show signs of significant damage, such as severe corrosion, cracks, or persistent leaks that cannot be repaired. Additionally, if performance enhancements are desired, upgrading to a high-performance charge pipe can yield substantial benefits. Consulting with a qualified professional can help determine the right course of action.
5. FAQs About What is a Charge Pipe
5.1 Charge Pipe vs. Other Pipes in the System
The charge pipe is often confused with other pipes in the turbocharging system, such as boost pipes and inlet pipes. While all these pipes play vital roles:
- Inlet Pipes: Route air from the air intake to the turbo.
- Boost Pipes: Carry compressed air from the turbo to the intercooler.
- Charge Pipes: Transport air from the intercooler to the intake manifold.
5.2 Does a Charge Pipe Add Horsepower?
While a charge pipe alone may not drastically add horsepower, replacing a factory charge pipe with a high-performance version can lead to better airflow, improved throttle response, and enhanced overall engine efficiency. These factors collectively can contribute to a measurable increase in horsepower, particularly when combined with other modifications.
5.3 How to Choose the Right Charge Pipe for Your Vehicle
When selecting a charge pipe, consider the following factors:
- Material: Choose between aluminum or stainless steel based on your driving conditions and goals.
- Diameter: Larger diameters can improve airflow, but ensure they fit within your vehicle’s specifications.
- Brand Compatibility: Ensure the charge pipe is compatible with your specific make and model for optimal performance.